Iron deficiency anemia is one of the nutritional deficiency diseases. However, some parents think that if they eat well and eat fine, how can children lack nutrition? This view is not comprehensive, and iron-deficiency anaemia not only affects the baby's health, but also jeopardizes the intellectual development, so it must be taken seriously. Baby iron deficiency can affect mental development How to prevent iron-deficiency anaemia is one of the most noteworthy issues in the early 1000 days of life (from fetal period to 2 years after birth). According to the “Nutrition Development Report for Children 0-6 Years Old in China (2012)â€, the prevalence of anaemia in children under 5 years of age in China is relatively high. Among them, the problem of anaemia in children under 2 years of age is even more acute, especially in children aged 6-24 months who suffer from anaemia. The highest rate of illness. All infants and young children have the possibility of iron deficiency anemia, but the baby is more dangerous with one or more of the following factors: Anemia, premature birth, twin births or multiple births, fetal blood loss, and late feeding of food supplements rich in iron during pregnancy , irrational diet and gastro-intestinal diseases, rapid growth, long-term chronic blood loss. All babies with these risk factors must not only strengthen the supply of iron, but also have physical examinations on time to detect iron deficiency anemia in a timely manner. To prevent iron-deficiency anemia in infants and young children, we must first start with pregnant mothers. 1. Iron nutrition should be strengthened during pregnancy to prevent anemia during pregnancy First of all, pregnant women should ingest iron-rich foods such as meat, animal liver and animal blood, as well as iron-fortified foods such as pregnant women's milk powder, iron soy sauce, and fortified flour. Second, starting from the third month of pregnancy, iron containing 60 mg of elemental iron was orally administered daily, if necessary, until postpartum. Finally, hemoglobin should be monitored during pregnancy. Once you have found anemia, you should follow the doctor's advice and quickly take iron supplements. In addition, delayed umbilical cord ligation for 2-3 minutes during childbirth can also increase infant iron reserves. 2. Baby preferred iron supplement food After the baby has started to add food supplements within 6 months, he should first use a food supplement rich in iron, mainly including baby rice noodles (fortified iron, first added), liver paste and meat puree (6 months of trial, 7 months of formal addition, up to 1 At the age of 25-50 grams per day). Fruit (mud) and vegetables (mud) contain vitamin C, which promotes iron absorption and should be added daily. It should be reminded that although eggs (yellow yolks) contain more iron, they are difficult to absorb (absorption rate is only 3%) and are prone to cause allergies. Therefore, early additions are not recommended and should be postponed until seven or eight months later. Home-made rice porridge, rice, noodles, etc. have very little iron and are not a good source of iron. 3 children's diet should be balanced with After 1 year old, baby's recipes are getting richer, but you should still consume 350-500 ml of milk per day, and you can't continue breastfeeding for children up to 2 years old. It is recommended to choose formula milk (fortified iron). On this basis, one egg, 50 grams of animal food, 100-150 grams of cereal, 150-200 grams of vegetables, 150-200 grams of fruit, and 20-25 grams of vegetable oil should be ingested daily. Only in this way can the requirements for diversification of dietary varieties and a balanced diet be met. 4. If necessary, give your baby iron The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) suggested in 2010 (this statement was also adopted by the Ministry of Health's “Technical Code for the Management of Child Nutritional Disease Managementâ€) that breast-fed infants must start daily iron supplementation from 4 months until the beginning of 6 months. Iron is provided by food supplements. However, in 2012, AAP revised the above recommendations and concluded that there is no need for additional iron supplements within 6 months of breastfeeding. Baby formula-fortified (iron-fortified) babies can get enough iron from milk powder and do not need to take iron. However, preterm infants (born at full 37 weeks prior to birth) or low birth weight infants (birth weight < 2.5 kg) have a different situation. Iron supplementation should begin at 4 weeks of age at a daily dose of 2 mg of "elemental iron." /kg body weight (for example, a baby weighing 7 kg will need to add 14 mg of iron per day) until 1 year of age (the total daily dose will not exceed 30 mg). In addition, irons are also recommended for babies born to pregnant women who have anaemia in pregnancy but have not been intervened. Children who have been diagnosed with iron-deficiency anaemia should receive oral iron 1-2 mg/kg body weight daily (the total daily dose should not exceed 30 mg). To choose between meals, 2-3 times oral. At the same time also take vitamin C to promote the absorption of iron. Iron deficiency anemia is one of the most common nutritional deficiencies, especially in infants and young children. Iron-deficiency anemia not only damages the baby's immunity, but also can lead to irreversible growth and cognitive retardation, especially affecting the exertion of intellectual potential and reducing learning ability. Ready-to-eat Double Packed Sweet Corn
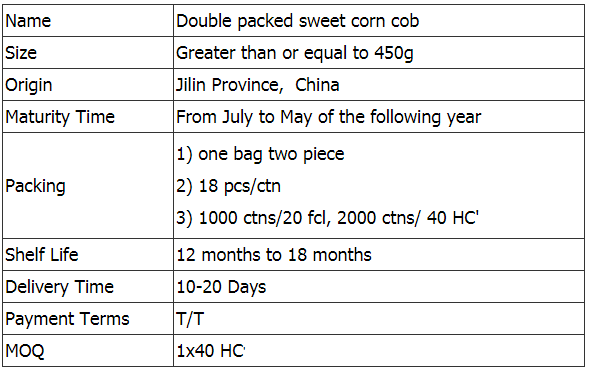
In this category is sweet corn from Jilin Province Agricultural Sister-in-law Food Co.
The physical characteristics of maize consist of grain colour, grain shape, seed coat lustre, grain length, grain width, 100 grain weight, grain diameter, uniformity of the seed and hardness. In most cases, the colour of the endosperm of mature maize kernels is yellow or white, while the seed coat and paste layer are colourless and transparent. Depending on the colour of the kernels, there are three types of maize: yellow, white and mixed. Depending on the kernel form, hardness and different uses, maize is divided into two types: common maize (hard, intermediate, horse-tooth, hard-horse, horse-hard) and special maize (high-lysine maize, high-oil maize, sweet maize, cracked maize, glutinous maize).
The sweet corn of Jilin Province Agricultural Sister-in-law Food Co., Ltd. belongs to the special corn category of yellow corn.
Also known as fruit corn. The leaves on the outside are light green (only the ears are in the pack, we have removed the leaves for you) and the kernels inside are white or yellow. Sweeter than regular sweet corn, but lower in starch and rich in vitamin E and fibre, which is anti-ageing and aids digestion. Perfect for eating raw, mixed with vegetables in salads; it can also be steamed, but don't cook it for too long, about 5 minutes.
If you have any questions, please contact us directly. If you have any questions, please email us directly.
Delectable Sweet Corn Cob,Microwave Sweet Corn Cob,Country Sweet Corn,Ready To Eat Sweet Corn Jilin Province Argricultural Sister-in-law Food Co., Ltd. , https://www.nscorn.com