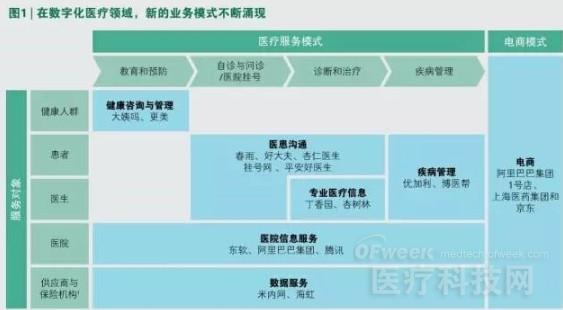
China's digital medical market will grow exponentially in the next five years, and the scale of application of digital medical care will reach nearly 700 billion yuan by 2020. In such a large environment, every link in the medical industry value chain will be affected, including the patient's diagnosis and treatment, the way doctors and hospitals work, and the supply of medicines and medical equipment. Companies in all parts of the value chain must make adjustments as soon as possible to adapt to the new situation. In 2014, China's digital medical market received a venture capital investment of about 4.5 billion yuan, ranging from pharmaceutical e-commerce, online communication services for doctors and patients, to disease management applications. And all this is just the beginning. With the development and utilization of various mobile technologies and Internet technologies, China's digital medical market will grow exponentially in order to better serve the medical market demand of China's 1.3 billion people. We expect that by 2020, this market size (according to the application of digital medical expenditure) will reach nearly 700 billion yuan, a significant increase from the level of about 20 billion yuan in 2014. In such a big environment, China's medical industry will undergo earth-shaking changes. Every aspect of the healthcare industry's value chain is affected, including the way patients are treated and managed, the way doctors work and the way the hospital operates, the way medicines and medical devices are supplied and used, and the structure and services of insurance institutions. Ways, etc. For the stakeholders in all aspects of the value chain, the changes and opportunities they face are also different. Some institutions and companies will have the opportunity to increase efficiency by “digitalizing†existing processes. Others will face more risk of being out. But for other organizations and companies, technological advances will help them create a new digital healthcare business. However, regardless of the category, all institutions and companies involved in the medical industry must explore new ideas and actively explore new business models: Digital companies that are new to the healthcare industry should actively seek to partner with hospitals, doctors, and other relevant organizations to leverage their mobile payment, social media, and search engine tools to gain a preemptive advantage in e-commerce and service models. Pharmaceutical companies and healthcare technology companies need to leverage digital tools to increase sales and marketing efforts, provide disease management solutions, and use big data analytics to support portfolio decisions and improve R&D efficiency. Companies also need to work with e-commerce companies to meet the growing consumer demand for medically-related products online. At present, consumers mainly purchase non-prescription drugs, health products and dietary supplements, as well as home medical device products online; in the future, consumers are also expected to purchase prescription drugs online. Pharmaceutical distributors and retailers must act quickly to avoid being replaced by e-commerce as an intermediary. Such companies face two choices: either to build their own e-commerce capabilities or to work with emerging e-commerce companies. Insurance institutions will have the opportunity to develop new services, including digital services, such as telemedicine consulting, to attract new customers in a short period of time. Such companies can also use big data analytics to reduce costs and improve patient outcomes over a long period of time. In the face of the digital transformation of the Chinese medical market, the above four categories of enterprises have the opportunity to play an important role in this process. One of the three trending trends in digital healthcare transformation is the widespread use of new technologies, such as mobile devices, cloud computing, and big data analytics. For example, in 2014, nearly 40% of China's population had smartphones, and they spent an average of three hours a day on smartphones. On this basis, the future will be complemented by ubiquitous high-speed Internet connectivity and big data resources, and companies will be able to provide a wide range of digital solutions for remote population monitoring and smartphone purchases for China's large population. The second trend is the Chinese government's unremitting efforts to address the long-standing inefficiencies of the health care system and to meet unmet needs – where digital healthcare can help. For example, telemedicine consultation and online appointment registration can help alleviate the overuse of medical resources in large hospitals, while the utilization of medical resources in small grassroots hospitals is low. In China, many patients still flock to large hospitals for basic needs such as renewal. ). In addition, in the long run, innovative solutions that help to continue effective communication between doctors and patients will also greatly improve the quality and level of patient care and management. The third trend is that the regulatory environment is getting better. In 2012, the Chinese Ministry of Health (now the National Health and Family Planning Commission) invested 60 billion yuan to develop electronic medical records (EMR) and improve hospital information systems. Since then, the Chinese government has continued to increase efforts to promote the development of digital medical care. For example, the Chinese government has lowered the threshold for e-commerce related businesses, making it easier to register online pharmacies. It is expected that by 2016, some prescription drugs are also expected to be sold online. In addition, the government has allowed medical institutions in some provinces to conduct pilot work for remote diagnosis and prescription drug prescribing. Current market structure and future development trends. Driven by the above three major trends, digital medical care is booming. Whether in the medical services field or in the e-commerce sector, various emerging business models are emerging. (See Figure 1.) Digital companies (including well-known large companies and start-ups) who are newly involved in the medical industry are the new force driving business model innovation. They have gradually occupied a place in the medical market and played an important role in shaping the digital medical market. effect. Take Baidu as an example. As a search engine company, Baidu actively uses its core business to provide medical health information to consumers, and provides consumers with access to online appointment registration and telemedicine consultation. In addition, Baidu also sells wearable smart devices through the Dulife brand. Through cooperation with the Beijing government, Baidu uses wearable smart devices to track and analyze Beijing citizens' health information, aiming to provide better health services for Beijing residents. Alibaba Group has incorporated online pharmacies into its e-commerce platform. At the same time, the group is developing and optimizing an application that will help patients use Alipay to purchase prescriptions online. In addition, the group is creating a new service platform to help doctors in medical institutions conduct remote care on the platform. Alibaba is also accelerating the Ali "Future Hospital" program to help hospitals realize the digital development of patient service processes. As a large social media company, Tencent is also expanding its social and payment platform, WeChat's business coverage, to extend the territory to the medical field. In 2014, Tencent launched the “Smart Healthcare†information technology platform to provide medical service processes on the Internet and mobile phones, including appointment registration and payment services. In addition, Tencent is actively investing in related companies (such as China's largest online network for medical professionals, “Clove Gardenâ€), which provides a full range of services for patients and doctors in all aspects of the value chain. At the same time, emerging companies with backgrounds in venture capital, such as Chun Yu and Almond Doctor, are also developing new service products such as telemedicine communication. As a traditional insurance company, Ping An Insurance Company of China has launched an application called “Ping An Good Doctor†to allow patients to consult with doctors remotely. Other traditional pharmaceutical distribution companies and retail companies such as Shanghai Pharmaceuticals are also actively exploring opportunities in the e-commerce sector. With the increasing number of newcomers and the increasing investment, the development momentum of digital medical care can not be underestimated. We expect China's digital medical market to maintain rapid growth in the next five years: by 2020, the market size will reach nearly 700 billion yuan (according to the application of digital medical expenditures). Among them, digital medical services accounted for the largest share, reaching about 600 billion yuan, and e-commerce will reach about 100 billion yuan. The growth of China's digital medical market is largely due to the transfer of expenditures originally used for offline services to digital channels. But the growth of the market is also due to new business models and sources of income. This growth will cover a large number of digital medical services, of which the largest increase in market size is the disease management and doctor-patient communication services, these two sectors will take shape. (See Figure 2) Digital disruptive forces will affect every aspect of the value chain. Of course, there are also a few factors that hinder the development of digital medical care in China. First, there are still uncertainties in the regulatory policies for telemedicine, online prescription drug sales, and patient reimbursement, which will delay the promotion of these services to some extent. In addition, the electronic medical record systems used in different hospitals are quite different, which will bring great challenges to the comprehensive networking of hospital databases. Moreover, China currently lacks sufficient experience in large-scale medical data management, so it will inevitably take some detours and need to undergo a rapid improvement process. Zinc Fortifier,Food Additive Zinc Sulfate,Zinc Sulfate Heptahydrate,Zinc Sulfate Monohydrate LIANYUNGANGLONGTAIWEI FOOD INGREDIENTS CO.,LTD. , https://www.longtaiweifood.com