hERG Potassium Channel High-Throughput Safety Screening - Molecular Devices IonWorks Barracuda
High-throughput safety screening of hERG potassium channel
——IonWorks Barracuda high-throughput automatic patch clamp system advantages of multiple sample detection methods

Features:
• Ultra-high throughput – for high-volume compound screening • Hourly > 6,000 data points • 384 simultaneous recordings • Ultra-low operating costs • Stable, reliable equipment • Low cost, efficient supplies • Continuously added per hole The concentration effect data recorded by the method is similar to the results of traditional manual patch clamp recording • Highly consistent, repeatable data,
• Patented Population Patch Clamp technology guarantees highly repeatable recording
Due to the potential risk of death after hERG (human ether-Ã -go-go gene) is inhibited, the importance of screening for candidate drug hERG safety in the early stages of drug development is increasingly highlighted. Traditional patch clamp techniques, which study the gold standard for ion channel activity and pharmacological properties, are clearly impractical for high volume screening requirements due to their high cost of operation, low throughput, and high operator requirements. Even after the rapid development of automatic patch clamp systems over the past decade, the high cost and relatively low flux factors have limited the safety screening of hERG ion channels.
The IonWorks Barracuda® fully automated patch clamp system provides pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies with a true solution for hERG ion channel safety screening of thousands of compounds at low cost, fast and efficient. The 384-parallel recording performance and low-cost consumables make IonWorks Barracuda an ideal device for medium- and high-throughput high-volume compound screening.
One of the features of the method of multiple injections per well is that the recorded dose-effect data is similar to that recorded by conventional manual patch clamps, so that the resulting data quality is more reliable. This method can be widely used in the study of a variety of ion channels, especially the study of the blocking effect of compounds in voltage-gated ion channels.
Research purposes
Multiple injections per well can increase throughput and save on compound screening costs. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of using the loading method in the safety screening of hERG compounds in the IonWorks Barracuda system and compare it to another single-point method per well in Barracuda.
The IonWorks Barracuda system supports up to 8 injections per stimulus, and the number of stimulations in an experiment is not limited, so there is virtually no limit to the number of additions per experiment.
When the pharmacological properties of the compound concentration effect are examined, a multiple cumulative loading method from a low concentration to a high concentration can be employed in each of the recording holes of the entire 384-well recording plate. This single hole repeating multiple loading method has several advantages:
• Increased throughput • Reduced costs • Consistent with traditional methods for detecting compounds acting on ion channel effects, multiple concentrations of compounds are added to each cell or record site and their continuous gradient concentration effects are detected.
A typical single-hole, 8-loading experiment takes approximately 30 minutes to produce >3000 data points, resulting in >6000 data points per hour.
The IonWorks Barracuda system can also be used to screen hERG safety compounds in a single plate and only once per well.
Under this method, 384 data points are acquired approximately every 20 minutes, resulting in >1100 data points per hour.
In order to effectively compare the pharmacological data of the above two methods, the experiment used a completely consistent hERG positive inhibitor and tested with 6 concentration gradients.
result
When comparing the pharmacological properties of the compound multi-concentration effect, the single-well multiple-loading method increased the flux by more than 4 times compared to the single-plate single-loading.
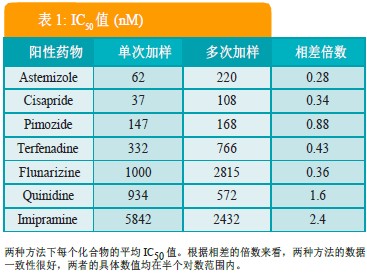
Positive inhibitors of 7 hERG channels were continuously added with 6 gradient concentrations in each recording well. The comparison of the results of the two loading methods (single loading and multiple loading) is shown in Table 1. The flux increased to 2,300 data points per experiment, with 4,600 data points per hour.
Materials and Method
Chinese hamster ovary cells (CHO) stably transfected with human Kv11.1 channels were obtained from ChanTest (Cleveland, OH). All reagents and drugs used in this experiment were from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO).
Development of multiple loading methods for hERG ion channels
In multiple injections, cells require multiple solution exchanges and prolonged voltage stimulation, increasing the likelihood of current rundown. In order to improve the stability of the cell recording after the test time is lengthened, a single pulse voltage stimulation scheme is used instead of the 5-time pulse voltage stimulation scheme in the original single-loading method. The compound was dissolved in the extracellular fluid at a concentration of 3 times the final concentration and contained 1% DMSO.
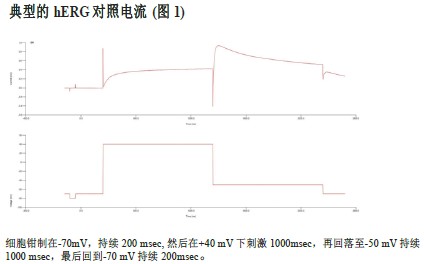
The recording wells were added to the final concentration after the experiment, and the concentration of DMSO was 0.33%. Compounds were added to the recording wells and incubated for one minute before voltage stimulation was initiated, +40 mV for one second, followed by a -50 mV stimulation for one second to detect tail current peaks (Figure 1). In one experiment, six compound plates of different concentration gradients were prepared, which facilitated the loading of the sample by 6 times. After confirmation of the complete experimental method, the selected 7 hERG-positive drugs were sequentially detected.
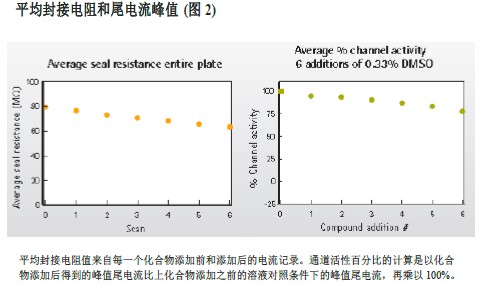
The record stability results of multiple loading experiments are shown in Figure 2. The figure shows the average sealing resistance of all 384 wells in one of the experiments, and the average channel activation level based on the tail current peak obtained after 6 times of the addition of 0.33% DMSO in 24 control wells.
Pharmacological properties of single-well multiple-loading methods: cumulative concentration effect data generated similar to traditional patch clamp technique
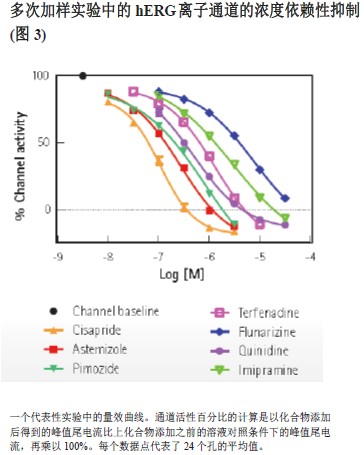
In the seven hERG-positive pharmacological validation experiments, six compound plates were continuously monitored for each experiment. Each compound plate has only one concentration of each compound to be tested, and each compound repeats 24 wells. The concentration of the first compound plate was the lowest, and the concentration of the sixth compound plate was the highest.
A dose-effect curve and corresponding IC50 values ​​were obtained in each of seven independent experiments. Figure 3 shows the pharmacokinetic curve obtained in a representative experiment.
Data repeatability detection of compound multiple addition method
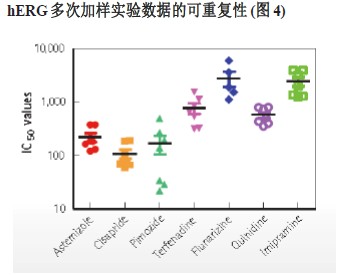
It is very important to screen the stability of the data in the experiment. The pharmacological data of all seven positive hERG inhibitors showed good reproducibility using the previously optimized experimental conditions. The stability of the six-time compound addition experiment is shown in Figure 4. This stability is particularly important and is reflected in the technical requirements for stable current recording after application and after application of voltage stimulation.
One of the positive drugs tested, Pimozide, was observed to be less than expected. This may be related to the high lipophilicity of the compound, resulting in instability of the compound in most plastic material environments during the screening process.
to sum up
This experiment verifies that the single-hole multiple-dosing method can significantly increase the flux and reduce the operating cost under the premise of ensuring data quality.
• Flux significantly increased from 1100 to 4,600 data points per hour.
• In terms of pharmacological results, the IC50 values ​​for single and multiple injections remained consistent.
• Stability and reproducibility throughout the experimental results • Cumulative concentration effect data is similar to traditional patch clamp technique
references
Application protocol: "Validation of the IonWorks Barracuda System for hERG Ion Channel Assay", by Karen Cook, MS, James L. Costantin, Ph.D., and Xin Jiang, Ph.D., Molecular Devices, LLC (2011)
The health benefits of capsicum include relief from cancer, peptic ulcer, menopausal problems, low risk of cardiovascular disease and diabetes. it has anti-inflammatory, analgesic properties and may also provide relief in pain related to arthritis. it also provides relief from fibromyalgia, skin aging and psoriasis. our quality is the best and we are offering them at promotional prices to expand on our market in your zone.
Red Chile,Red Hot Peppers,Red Chili Pepper,Red Chilli Pepper
Jining Yuanheng International Trading Co.,Ltd , https://www.garlic-factory.com