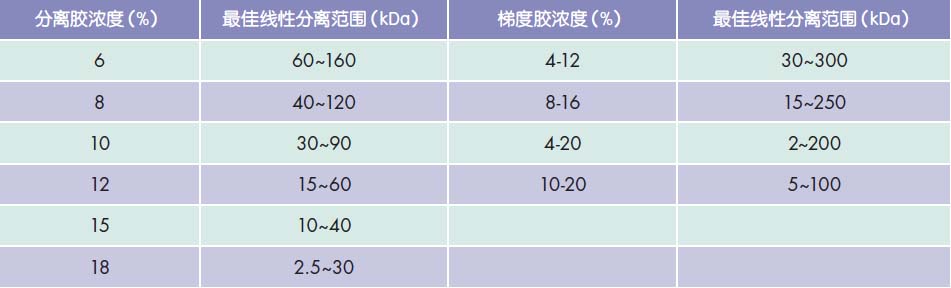
Protein extraction Protein sample extraction is the basis for protein quantification and analysis. Natural proteins have different molecular structures and chemical properties. It is important to select appropriate cell lysates for protein samples. When selecting a cell lysate, besides considering the protein yield, consider whether the selected primary antibody recognizes a linear epitope. Some protein lysates containing sodium dodecyl sulfate ( SDS ) and strong ion detergents (such as sodium deoxycholate) can extract a large amount of protein from tissues or cells, suitable for PAGE , Western blot and other detection; However, since such lysates tend to denature proteins, they are not suitable for experiments such as co-immunoprecipitation ( Co-IP ). When using antibodies that recognize only non-denatured epitopes , lysates that do not contain detergents or contain milder non-ionic detergents (eg NP-40 , Triton X-100, etc.) should be selected . Protein lysates containing SDS and strong ion detergents cannot be used . Protein concentration determination Determining protein sample concentrations is critical for many experiments. Usually the concentration of most protein samples can be quantified by colorimetric assays. According to the principle of color change caused by the combination of some special chemical reagents and proteins, the absorbance at a specific wavelength is detected by a spectrophotometer or a microplate reader, and the protein content in the sample can be converted by comparing with a protein standard. Bradford Protein Quantitative Reagent ( Cat. No. E161-01 ) is highly sensitive, simple, fast, and inexpensive; BCA Protein Quantitative Reagent ( Cat. No. E162-01 ) provides higher sensitivity and accuracy, and It is more suitable for the determination of trace proteins by the influence of detergent. Protein electrophoresis and Western blot Electrophoresis is the separation of proteins, an important method of identifying molecular weight and concentration of protein, in particular polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (Po l yac ry lamide Ge l Electrophoresis, PAGE). Acrylamide and methylidene bisacrylamide can be polymerized to form a network polymer having a molecular sieve effect as a solid phase support for electrophoresis. When performing non-denaturing PAGE ( Native PAGE ), the protein remains intact during electrophoresis and is separated by three factors: molecular weight, shape, and charge. An anionic detergent SDS as a denaturing agent and a solubilizing agent was added to the denaturing PAGE ( SDS-PAGE ) . On the one hand, SDS can open the intramolecular and intermolecular hydrogen bonds of proteins, destroy the secondary and tertiary structure of proteins, and eliminate the difference in shape between proteins; on the other hand, it can be combined with the depolymerized amino acid side chains to make proteins The negative charge carried by the -SDS complex greatly exceeds the charge of the protein itself, eliminating the difference in charge between proteins. Therefore, in SDS-PAGE , the rate of protein migration under an electric field is only related to its molecular weight. Optimal linear separation range for different concentrations of Tris-Glycine gel Immunoblotting (Western blot) is to identify proteins and peptides, and detecting the protein expression levels common means. The technique generally involves transferring a protein or polypeptide molecule separated by PAGE onto a solid phase carrier ( PVDF membrane or nitrocellulose membrane), and performing an immune reaction by a specific antibody (primary antibody) of the target protein, and then labeling with the enzyme. The second antibody (secondary antibody) reacts to develop a color or luminescence through the substrate, thereby detecting a specific target protein. Antimicrobial Hemodialysis Catheter Hemodialysis Catheter,dialysis Catheter,powertrialysis dialysis catheter,peritoneal dialysis catheter,dialysis catheter kit Anesthesia Medical Co., Ltd. , https://www.honestymed.com